The
Long(er) View in 2014
When making any decisions about the
future, one needs to look at long term trends, medium term episodes
and short term events. They all guide where we are likely to be in a
few years/ decades. Also, important is to understand the trends that
will happen no matter what, and other things that will seek to
counter-balance or reinforce these trends. In many cases, unraveling
of some trends will set off domino effects that will fundamentally
alter the reality that we see.
Overall trends can be assessed in the
following areas.
- Demographics
- Technology
- Science
- Energy
- Economy
- Social
- Politics
Out of the above, I would rate
Demographic trends to be most fundamental. Science and Technology
follow a close second. The remaining – Economic, Social and
Political trends to me are generated out of the more fundamental
forces that are likely to be more kosher.
Demographic trends in the next decade
The demographic trends in the near
future is almost clear. With 2.5 out of the 7 billion people on the
planet (37%) living in China and India, the world's population is
becoming more skewed towards South East Asia.
A more fair comparison would be the density of population.
Also, if we compared the population in East and South East Asia, we would find them to be comparable.
For most of the world population (including China), fertility rate is 1-2 births per woman. Also, world population growth rates around the world hover from -ve to 1-2% in most of the planet. So, what does all this mean?
 |
| Global Population by country in 2013 |
 |
| Global Population Density |
Also, if we compared the population in East and South East Asia, we would find them to be comparable.
For most of the world population (including China), fertility rate is 1-2 births per woman. Also, world population growth rates around the world hover from -ve to 1-2% in most of the planet. So, what does all this mean?
Next the median age in different countries of the world.
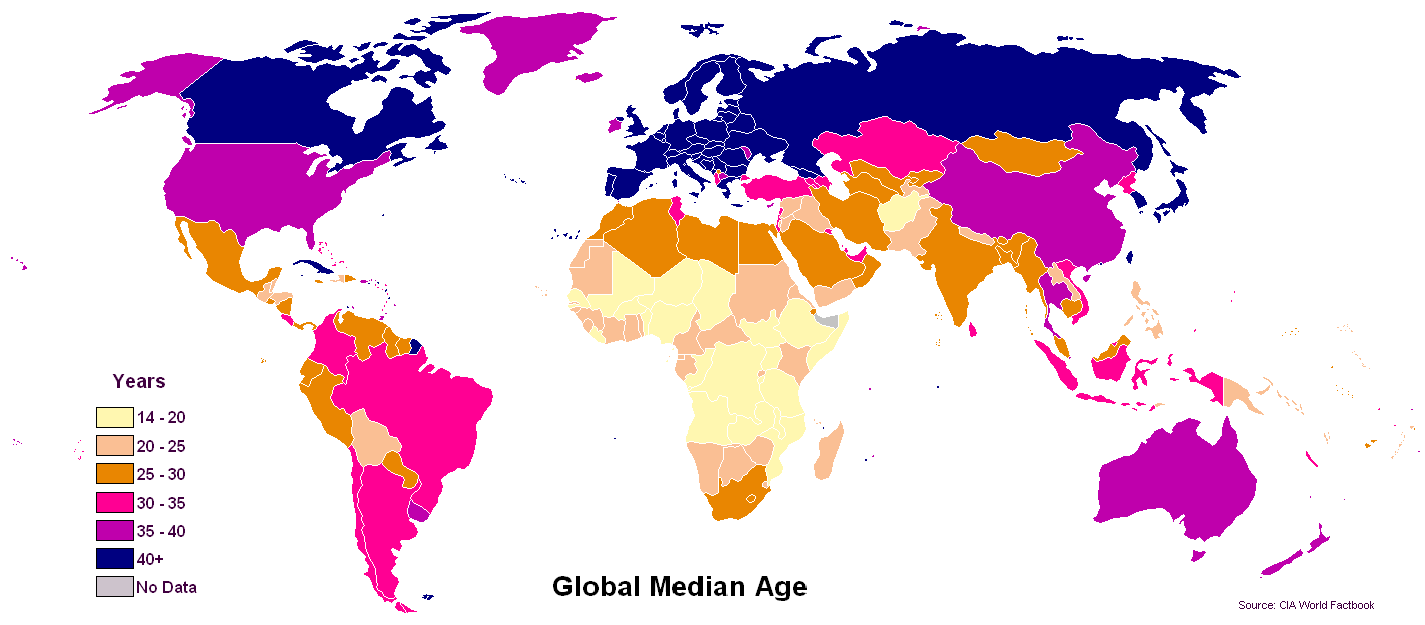
It means that there will be more older people in richer parts of the world, while more working/ younger population in poorer parts of the world. While a small percentage of the working population may choose to take care of the old and rich, it is more likely that the now older and retiring population would want the younger population to take care of them. This could happen through the following ways
- Healthcare professions may become more lucrative for younger population
- More automation and technology coming into healthcare
- More investment into training and education of younger people in health and medical disciplines.
- Establishment of large healthcare organizations that may provide direct employment opportunities to working populations in current countries.
- Manufacturing and innovation moving to more populous countries in Asia and Africa
- It will also be important for currencies to stay favourable for enticing younger populations to focus overseas.
If we see global expenditures on health
as percentage of GDP, we can see the following trend.
 |
| Health Expenditure as a percentage of GDP by country matches the median age distribution shown above with some minor variations |
Technology Trends
Technology is disrupting the economics
of many fundamental value chains. Steve Jobs idea of modeling Apple
on Sony instead of Microsoft, upon his return to Apple, and then
using technology to try and disrupt each and every industry Sony was
in (almost), including music, media and entertainment is a case in
point.
As technology evolves, the threshold
economics of many traditional industries will give way. Industries
such as Banking (online banking), Trading (online), Finance, Higher
education (MOOCS), Insurance (Geico), Entertainment (Netflix and
YouTube), Print Media (websites, Facebook, declining advertising and
readership), etc. have already felt the tectonic plates shift with
communication and Internet technology. As new platforms emerge, they
unravel the economics of previous business models and allow new
businesses to emerge.
Mobile
New changes will likely be increased
adoption of 3G and 4G technologies in mobile. Current adoption is 30%
in markets where 3G is deployed, and 4G deployment is accelerating as
people are accessing more online services on their mobile. It is
likely in next few years, 3G and 4G adoption will grow substantially.
This is more true for areas where no other competing technologies
such as television and fixed line phones and Internet have been
deployed.
Also, as the mobile phone batteries
improve, processing improves and demand for gaming and media
consumption on mobile increases, it is likely that the phones will
become bigger and adoption of smart phones will increase. Also, as TV
content becomes more accessible on smart phones, it is likely that
the smart phone user base will grow beyond urban to more broad-based
as for traditional Television audience.
 |
| Smartphone adoption will rise across all countries with additional services coming on line. |
Automobile Technology
Automobile technologies are increasing
range and reducing price of electric vehicles. Tesla motors seems to
be eying a more sizable percentage of the market in coming years, and
other vendors are also investing in making traditional combustion
engines, hybrids and electric vehicles more economic in terms of cost
of ownership. Pure electric cars now provide a range of 300 miles at
a full charge that costs 9 dollars on average.
In other countries, which are not producing their own oil (and hence have to rely largely on oil imports), the move to mass transit modes will intensify specially in urban areas. Given congestion and cost for travel, it is also likely that electronic commerce and e-delivery will intensify. In some countries, where the logistics and distribution is not well developed, online retailers may partner with brick and mortar companies to promote last mile delivery. Given these scenarios, it is likely that mobile commerce will also intensify.
In other countries, which are not producing their own oil (and hence have to rely largely on oil imports), the move to mass transit modes will intensify specially in urban areas. Given congestion and cost for travel, it is also likely that electronic commerce and e-delivery will intensify. In some countries, where the logistics and distribution is not well developed, online retailers may partner with brick and mortar companies to promote last mile delivery. Given these scenarios, it is likely that mobile commerce will also intensify.
Internet
There is wide disparity between
countries in terms of per capita bandwidth consumption. This is an
image from 2003, however this is perhaps indicative of the order of magnitude.
Given the economic realities that
underpin these innovations, it seems most likely that these
innovations will intensify. In the short and medium term, companies
will benefit from capital investment in last mile connectivity.
Science trends
Much of scientific research is focused
on medicine and health. This is a space I need to do more research to
understand the trends a little deeper.
Energy Trends
Energy trends are a little mixed at
this point. The ongoing exploration and extraction of oil and gas in
continental North America and in Russia is likely to put pressure on
OPEC. However, these efforts need oil to stay above 80 to 100 dollars
per barrel. Therefore, it is unlikely that price of oil is going to
change even with US and Europe reducing their reliance on middle
eastern oil. This will make alternative energy sources more appealing
including solar, wind and others. Also, as the adoption of electric
vehicles increases, it is likely that solar adoption will increase
both at grid as well as consumer side. On the consumer side, we can
expect households, offices, plugin charging stations increase their
adoption of solar and other alternative forms of energy.
Given new alternative forms of energy
sources coming online, it is anticipated that power grids will be
re-balanced to allow grids to tap into new forms of energy.
Initiatives such as Smart grid roll outs will see investments in
digitization and improvement in reliability of the grid. Smart grid
drivers seem to be of two kinds – firstly, introducing Demand
Responsive capabilities and secondly, Supply Responsive capabilities.
Given energy efficiency is improving across most usage scenarios
coupled with Time of use pricing, it is likely that Supply Responsive
measures will be a bigger driver for change to the Grids.
That now leaves Economy, Social and
Political trends that we will cover in the next post.



